Tooth Decay | Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & Prevention

Why Tooth Decay Deserves Your Attention
Tooth decay is one of the most common dental problems in the world, yet it’s also one of the most preventable. From white spots that indicate early enamel damage to black lines that signal advanced decay, understanding the progression of cavities can help you take control of your oral health.
This pillar page brings together everything you need to know about tooth decay — causes, stages, prevention, and treatments — while linking to detailed guides that answer specific questions.
1. What is Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, happens when bacteria in your mouth produce acids that erode the enamel, leading to permanent damage if untreated.
Key points:
-
Caused by bacteria + sugar + poor oral hygiene.
-
Progresses slowly, often unnoticed in early stages.
-
Can affect anyone — children, adults, and seniors alike.
2. How Does Tooth Decay Start?
Decay begins with plaque — a sticky film of bacteria. When you eat foods high in sugar or starch, the bacteria feed on these and release acid. Over time, this acid:
-
Weakens enamel (early white spots).
-
Reaches dentin (causing sensitivity).
-
Advances to the pulp (severe pain or infection).
👉 Related Post:
White Spots on Teeth: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
3. Early Warning Signs of Tooth Decay
Recognizing the first signs of decay can save your teeth. Common symptoms include:
-
White or chalky spots on enamel.
-
Tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods.
-
Grey or black discoloration.
-
Pain when chewing or moving your head.
👉 Related Post:
Grey Spots on Teeth and Molar Tooth Stains: Causes & Treatment
👉 Related Post:
Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Move My Head or Walk
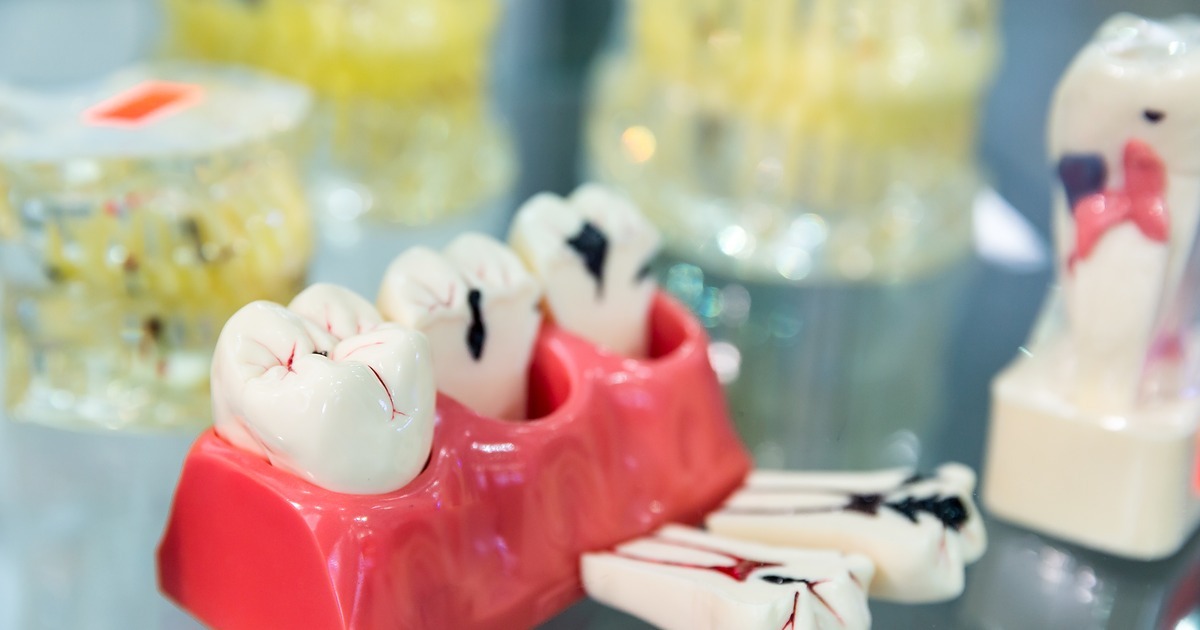
4. Advanced Signs of Tooth Decay
If left untreated, tooth decay gets worse:
-
Black lines or streaks appear.
-
Teeth may start rotting from the inside out.
-
Cavities deepen, causing constant pain.
-
Infection may spread to gums or jawbone.
👉 Related Post:
Black Lines on Teeth: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
👉 Related Post:
Teeth Rotting from Inside Out: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
5. Risk Factors for Tooth Decay
Some people are more vulnerable to decay than others. Common risk factors include:
-
Poor brushing and flossing habits.
-
High sugar and acidic diet.
-
Dry mouth (low saliva production).
-
Lack of fluoride exposure.
-
Genetics and enamel strength.
-
Frequent snacking or sipping sugary drinks.
6. Stages of Tooth Decay (Suggested Subpage)
Tooth decay typically progresses in 5 stages:
-
Demineralization – white spots on teeth.
-
Enamel Decay – visible stains or pits.
-
Dentin Decay – increased sensitivity.
-
Pulp Damage – severe toothache.
-
Abscess Formation – infection spreads beyond the tooth.
👉 Suggested New Subpage: “Stages of Tooth Decay: From White Spots to Cavities.”
7. Tooth Decay in Children vs. Adults (Suggested Subpage)
-
Children: Higher risk due to sugary snacks and weaker enamel.
-
Adults: Risk increases with gum recession and worn enamel.
-
Seniors: Dry mouth from medications makes cavities more likely.
👉 Suggested New Subpage: “Tooth Decay in Children: Prevention and Treatment Tips.”
8. Can Tooth Decay Be Reversed?
Yes — but only in the early stages. White spot lesions may remineralize with:
-
Fluoride treatments.
-
Remineralizing toothpaste.
-
Diet changes (reduce sugar).
-
Professional dental cleanings.
Once a cavity forms, you’ll need restorative treatments like fillings or crowns.
👉 Related Post:
White Spots on Teeth: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
9. Treatments for Tooth Decay
The right treatment depends on the severity:
-
Fluoride treatments – strengthen enamel in early decay.
-
Dental fillings – restore small to medium cavities.
-
Crowns – for large decay or weakened teeth.
-
Root canal therapy – if decay reaches the pulp.
-
Extraction – when the tooth cannot be saved.
👉 Suggested New Subpage: “Dental Filling Cost: How Much Does a Cavity Filling Cost?”
10. Prevention of Tooth Decay
Preventing cavities is easier than treating them. Best practices include:
-
Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
-
Flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth.
-
Limiting sugary foods and drinks.
-
Drinking water instead of soda or juice.
-
Visiting your dentist every 6 months.
👉 Suggested New Subpage: “How to Prevent Tooth Decay Naturally.”
11. Tooth Decay Complications if Left Untreated
Ignoring cavities can lead to:
-
Severe pain.
-
Tooth abscess.
-
Spread of infection to jawbone or bloodstream.
-
Tooth loss.
-
Expensive treatments later on.
12. Suggested Additional Subpages for Stronger SEO Cluster
To make your Tooth Decay pillar page unbeatable, you can add:
-
“Early Signs of Tooth Decay You Shouldn’t Ignore.”
-
“Natural Remedies for Tooth Decay: What Works and What Doesn’t.”
-
“Is Tooth Decay Contagious?”
-
“How Diet Affects Tooth Decay.”
These will interlink perfectly with your current subpages.
Conclusion: Protect Your Smile from Tooth Decay
Tooth decay may be common, but it’s not inevitable. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments, you can take proactive steps to protect your teeth.
Whether you’re dealing with white spots, black lines, or even teeth rotting from the inside out, early action can save your smile — and your wallet.
👉 Explore the detailed guides linked in this post to get practical solutions for every stage of tooth decay.